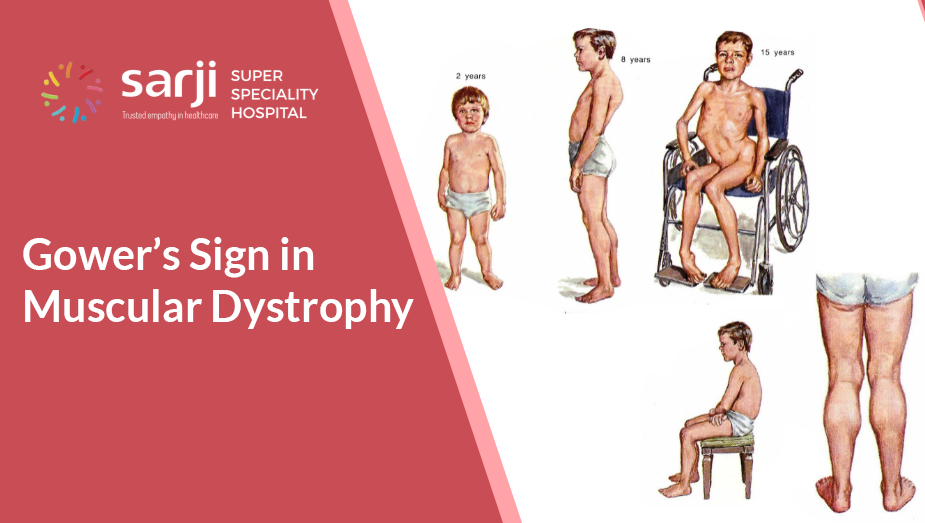
Ever noticed a child using their hands to push on their legs to stand up? This is Gower’s maneuver, a classic sign of muscle weakness, often seen in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). Early detection can help in better management.
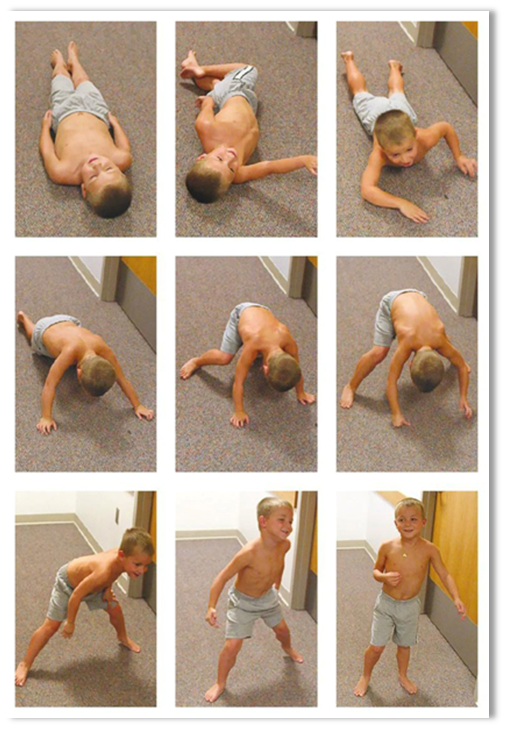

If such signs are present with a child, it is recommended to consult a physiotherapist or neurologist for evaluation.
Physiotherapy Rehabilitation Protocol for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a progressive neuromuscular disorder requiring a structured physiotherapy plan to maintain function, prevent contractures, and improve quality of life. Below is a step-by-step rehabilitation protocol for individuals with DMD at different stages.
1. Early Phase (Ambulatory Stage)
Goal: Maintain strength, flexibility, and functional mobility while delaying progression.
Assessment:
- Baseline muscle strength (Manual Muscle Testing, MMT)
- Range of motion (ROM) assessment
- Gait analysis
- Functional tests (e.g., 6-minute walk test, North Star Ambulatory Assessment)
Intervention:
1. Stretching & Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises
- Passive stretching of gastrocnemius, hamstrings, hip flexors, and iliotibial band to prevent contractures.
- Performed daily (3–5 reps, 30 seconds each).
2. Strength Training (Submaximal & Low-Resistance)
- Focus on proximal muscle groups (e.g., glutes, quadriceps).
- Avoid eccentric exercises to prevent muscle damage.
- Functional movements like sit-to-stand and stair climbing.
3. Gait & Posture Training
- Encourage heel cord stretching to prevent equinus deformity.
- Use of orthotic devices (AFOs) to prevent foot drop.
- Promote proper posture to prevent lumbar lordosis.
4. Breathing Exercises
- Diaphragmatic breathing to improve respiratory function.
- Blowing exercises (balloons, spirometer) to enhance lung capacity.
5. Hydrotherapy (Optional)
- Low-impact exercise to improve mobility and reduce joint stress.
2. Transitional Phase (Loss of Ambulation, Early Non-Ambulatory)
Goal: Prevent contractures, support respiratory function, and maintain independence.
Assessment:
- Joint contractures (hip flexors, knees, and ankles)
- Pulmonary function (spirometry, cough strength)
- ADL assessment (eating, dressing, transfers)
Intervention:
1. Passive Stretching & Positioning
- Maintain joint mobility and prevent scoliosis.
- Night splints/AFOs to prevent ankle contractures.
2. Respiratory Physiotherapy
- Assisted cough techniques (manual and mechanical).
- Breathing exercises with inspiratory muscle training.
3. Seated Mobility & Transfers
- Wheelchair training (posture support, cushion adjustments).
- Transfer techniques to reduce caregiver burden.
4. Functional Independence Training
- Adaptive equipment (feeding aids, dressing supports).
- Occupational therapy for daily activity modifications.
3. Late Phase (Advanced Non-Ambulatory Stage)
Goal: Optimize comfort, respiratory support, and prevent complications.
Assessment:
- Severe contractures and scoliosis progression
- Respiratory decline (oxygen saturation, cough ability)
- Nutritional intake and swallowing assessment
Intervention:
1. Contracture & Pain Management
- Positioning with custom seating systems.
- Passive ROM exercises to reduce stiffness.
- Pain relief techniques (heat therapy, massage).
2. Advanced Respiratory Support
- Non-invasive ventilation (BiPAP/CPAP).
- Airway clearance techniques (mechanical cough assist).
- Suctioning and secretion management.
3. Palliative & Supportive Care
- Psychological support for the patient and caregivers.
- Quality-of-life interventions (music therapy, relaxation techniques).
- Hospice care when required.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy in DMD focuses on maintaining mobility, preventing complications, and optimizing quality of life. A multidisciplinary approach with physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and respiratory specialists ensures comprehensive care tailored to the individual’s progression.