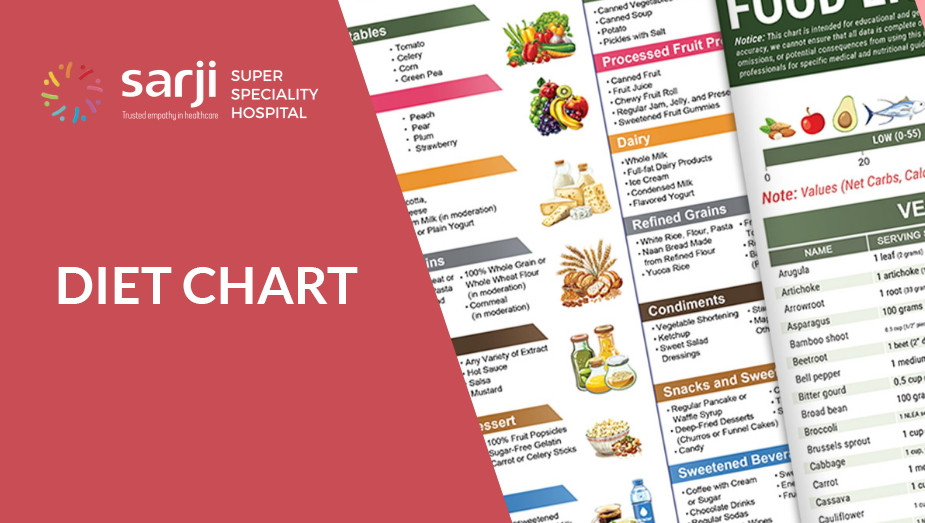
A diet chart is a structured and personalized plan that outlines the types, quantities, and timing of meals and snacks to be consumed over a specific period. It is designed to meet an individual's nutritional needs, health goals, and dietary preferences, ensuring a balanced intake of essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, fiber and minerals.
Diet charts are often created by dieticians or nutritionists and are tailored to address specific objectives, such as weight management, fitness enhancement, or medical conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or digestive disorders and many chronic diseases. They serve as a guide to promote healthy eating habits and maintain overall well-being.
IMPORTANCE OF MAINTAINING DIET CHART:
Maintaining diet charts is important for the following reasons:
1. Promotes Balanced Nutrition: Ensures a proper intake of essential nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals in the right proportions.
2. Supports Health Goals: Helps achieve specific objectives such as weight management, muscle building, or improving fitness levels.
3. Manages Medical Conditions: Tailored diet charts aid in controlling conditions like diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and digestive issues.
4. Encourages Healthy Eating Habits: Builds a routine for consistent, mindful, and portion-controlled eating.
5. Prevents Nutritional Deficiencies: Ensures that no essential nutrient is overlooked, reducing the risk of deficiencies.
6. Improves Energy Levels: Maintains steady energy throughout the day by planning meals and snacks effectively.
7. Aids in Digestive Health: Incorporates fiber-rich and easily digestible foods for a healthy gut.
8. Enhances Lifestyle Quality: Encourages long-term sustainable eating habits, improving overall health and well-being.
Diet charts provide a structured framework for healthy eating, making it easier to maintain and improve health consistently
TYPES OF DIET:
There are several types of diets, each designed to achieve specific health goals or cater to particular nutritional needs. Here are some common types of diets:
1. Balanced Diet
Purpose: To provide the right amounts of nutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals) needed for overall health.
Includes: A variety of foods from all food groups: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Benefits: Maintains optimal body function, supports energy levels, and prevents nutritional deficiencies.
2. Low-Carb Diet
Purpose: To reduce the intake of carbohydrates to promote weight loss and improve blood sugar control.
Includes: Foods high in protein and fats (e.g., meat, fish, eggs, cheese, and low-carb vegetables) while limiting high-carb foods like bread, pasta, and sugary snacks.
Benefits: Aids weight loss, controls blood sugar levels, and may improve metabolic health.
3. Vegetarian Diet
Purpose: Excludes meat, poultry, and fish, focusing on plant-based foods.
Includes: Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, milk and milk products, nuts, and seeds.
Benefits: Reduces the risk of heart disease, promotes digestive health, and is associated with lower cancer rates and better weight management.
4. Vegan Diet
Purpose: Excludes all animal products, including dairy and eggs.
Includes: Plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Benefits: Reduces the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers, while being more environmentally sustainable.
5. Mediterranean Diet
Purpose: Inspired by the traditional eating habits of people living in the Mediterranean region, focusing on heart-healthy foods.
Includes: High intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, olive oil, fish, and moderate consumption of red wine.
Benefits: Supports heart health, reduces the risk of chronic diseases, and promotes longevity.
6. Keto Diet
Purpose: To induce a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
Includes: High-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate foods (e.g., fatty meats, cheese, oils, and non-starchy vegetables).
Benefits: Promotes rapid weight loss, improves mental clarity, and can help manage epilepsy and type 2 diabetes.
7. Intermittent Fasting
Purpose: Involves cycles of fasting and eating, focusing on when you eat rather than what you eat.
Includes: No specific food restrictions; rather, it focuses on time-restricted eating, such as eating within an 8-hour window and fasting for 16 hours.
Benefits: Helps with weight loss, improves metabolism, and may have health benefits such as better heart health and improved insulin sensitivity.
8. Gluten-Free Diet
Purpose: To eliminate gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, to manage celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Includes: Gluten-free grains (e.g., rice, quinoa, and corn), fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy.
Benefits: Essential for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, helps reduce digestive issues, fatigue, and joint pain.
9. DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)
Purpose: Designed to reduce high blood pressure and improve heart health.
Includes: Emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while limiting sodium, red meat, and processed foods.
Benefits: Lowers blood pressure, reduces the risk of heart disease, and promotes overall cardiovascular health.
10. Flexitarian Diet
Purpose: Primarily plant-based but allows occasional meat or animal products.
Includes: Mostly plant-based foods (fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts) with occasional inclusion of animal products.
Benefits: Encourages plant-based eating without full commitment, promotes weight loss, and is heart-healthy.
11. Low-Fat Diet
Purpose: To reduce the intake of fats, particularly saturated fats and trans fats, to lower the risk of heart disease.
Includes: Low-fat dairy, lean meats, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Benefits: Helps reduce cholesterol levels, supports weight loss, and lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
12. Raw Food Diet
Purpose: Focuses on consuming unprocessed and uncooked foods to preserve their nutrients.
Includes: Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and sprouted grains. Some may include raw dairy, eggs, or fish.
Benefits: Promotes weight loss, improves digestion, and boosts energy levels.
Different diets serve different purposes depending on individual health goals, preferences, and medical conditions. It's important to choose a diet that aligns with your specific needs, lifestyle, and long-term health objectives. Always consider consulting with a dietician or nutritionist before starting any new diet, especially if you have underlying health issues.