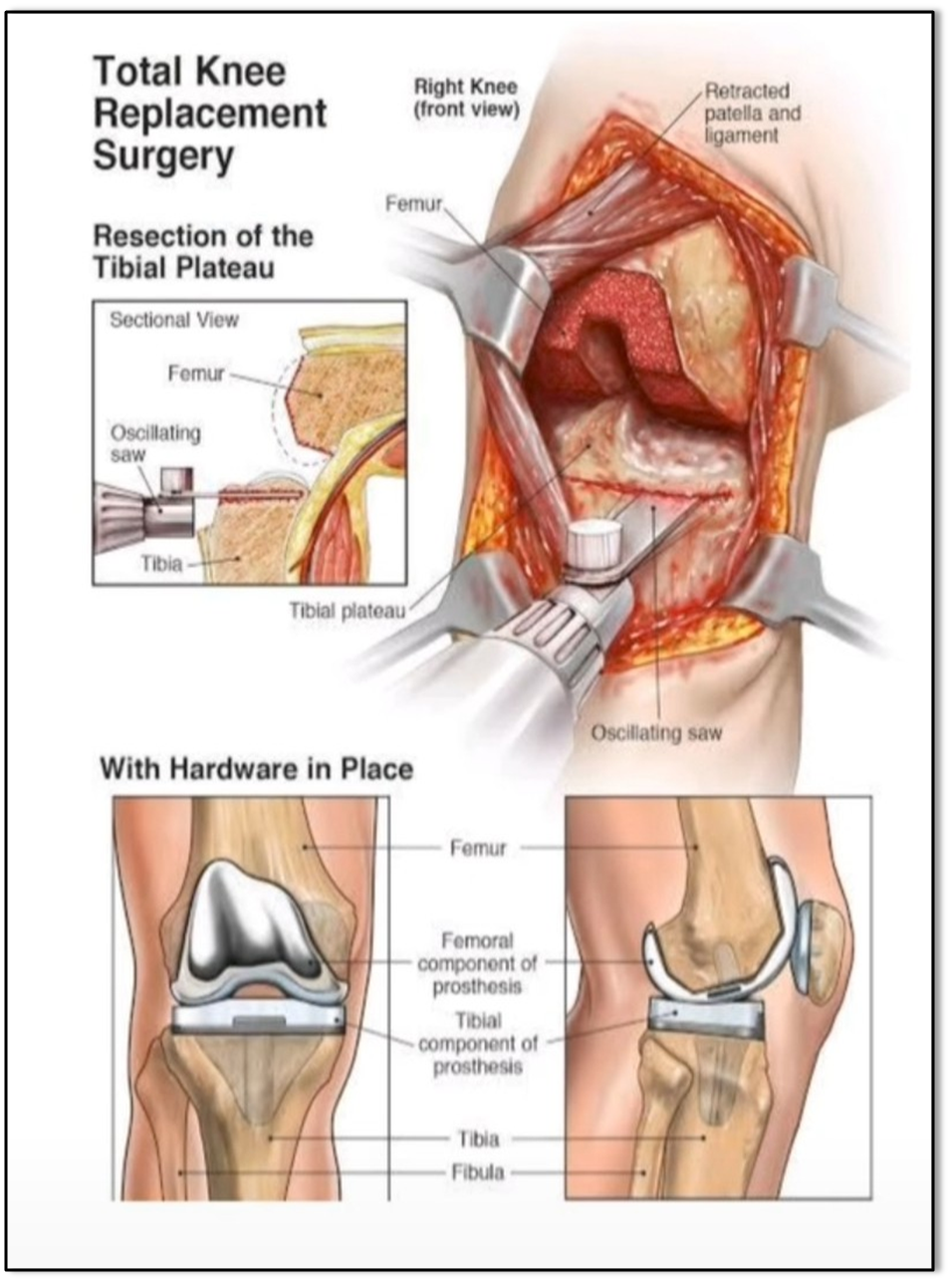
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT (TKR)
Pre – Operative Physiotherapy Management
Objectives:
- Prepare the patient physically and mentally for surgery.
- Enhance post-operative recovery potential.
- Educate on post – surgical expectations and rehabilitation process.
- Patient Education
- Understand the procedure: Explain the TKR process, expected outcomes, and the importance of rehabilitation.
- Goals of Physiotherapy: Discuss the role of physiotherapy in enhancing recovery and restoring function.
- Assessment
- Initial Evaluation: Assess range of motion (ROM), strength, gait, balance, and functional mobility.
- Set Baseline Measurements: Document knee flexion an extension, strength levels, and any functional limitations.
- Exercises
Range of Motion Exercises:
- Heel Slides: To improve knee flexion.
- Straight Leg Raises: Strengthen quadriceps.
Strengthening Exercises:
Quadriceps Isometric Contractions: To maintain muscle tone.
- Bridging Exercises: To strengthen hip extensors.
- Aerobic Conditioning: Encourage low-impact aerobic activities (e.g., walking, stationary biking) to improve overall fitness.
- Balance Training: Simple balance exercises to enhance stability.
- Functional Training
- Transfer Training: Teach safe techniques for getting in and out of bed and chairs.
- Gait Training: Practice walking with any assistive devices (e.g., walker) to improve confidence.
- Home Exercise Program
Provide a personalized home exercise program to maintain activity levels and prepare for post-operative rehabilitation.
Post – Operative Physiotherapy Management
Objectives:
- Control pain and swelling.
- Restore range of motion and strength.
- Enhance mobility and functional independence.
- Immediate Post-Operative Phase (Days 1 – 7)
Goals:
- Promote early mobility.
- Prevent complications.
Activities:
- Pain Management: Utilize ice therapy and medications as prescribed.
- Education: Reinforce information about the surgery and recovery process.
- Positioning: Keep the leg elevated to reduce swelling.
Gentle ROM Exercises:
- Ankle Pumps: To encourage circulation.
- Heel Slides: Initiate early knee flexion.
Strengthening:
- Isometric Quadriceps Exercises: Hold contractions for several seconds.
Mobility Training:
- Begin walking with assistive devices, focusing on weight-bearing as tolerated.
- Transfer training: Reinforce safe transfer techniques.
- Early Recovery Phase (Weeks 1-2)
Goals:
- Increase range of motion and strength.
Activities:
- Continue Ice Therapy and elevate the leg as needed.
Active ROM Exercises:
- Heel Slides: Aim for increased flexion.
- Sitting Knee Extension: Gradually extend the knee while seated.
Weight Bearing:
- Encourage gradual weight-bearing as tolerated.
Strengthening Exercises:
- Bridging: Enhance hip and core stability.
- Leg Raises: Focus on straight leg raises.
- Gait Training: Reinforce a normal walking pattern with assistive devices.
- Intermediate Recovery Phase (Weeks 3-4)
Goals:
- Improve strength.
- Functional mobility.
Activities:
- Continue ROM Exercises: Aim for 90-100 degrees of flexion.
Strengthening Exercises:
- Step-ups: Gradually increase height for progression.
- Wall Slides: Enhance knee flexion strength.
Cardiovascular Conditioning:
- Stationary Bike: Start low resistance biking to promote endurance.
Balance Exercises:
- Introduce more challenging balance activities (e.g., single-leg stands).
Functional Activities:
- Begin practicing stair climbing and sit-to-stand transitions.
- Advanced Recovery Phase (Weeks 5-12)
Goals:
- Restore strength.
- Endurance.
- Functional independence.
Activities:
- Progressive Strength Training: Use resistance bands and weights for exercises.
- Aerobic Conditioning: Continue low-impact activities (e.g., swimming, walking).
Functional Training:
- Complex movements (e.g., squats, lunges) and daily activities.
- Gait Training: Focus on normalization gait without assistive devices.
- Sport-Specific Activities: Gradual reintroduction based on patient’s lifestyle.
Key Considerations:
- Individualization:Tailor rehabilitation plans based on the patient’s progress and specific needs.
- Pain Management:Regularly assess and manage pain levels throughout recovery.
- Education:Reinforce the importance of adherence to the exercise program and strategies for joint protection.
- Monitoring Progress:Regular assessments of strength, ROM, and functional capabilities to adapt the rehabilitation plan.